- INTRODUCTION
- PURPOSE
- OBJECTIVES
- COMMITTEE
- CHAIR-COMMITTEE-MOM
- ACTIVITIES
INTRODUCTION
In order to foster a thorough understanding of media practices and related fields, the Tecnia Institute of Advanced Studies established a Center of Media Practices in 2022.
A “Centre of Media Practices” generally refers to a TIAS, Department of Journalism and Mass Communication or facility dedicated to the promotion and advancement of excellence in media-related activities. This can encompass various areas of the media industry, including Print Media, Electronic Media, Integrated Marketing, New Media, and Media Research (journalism, broadcasting, digital media, film production, advertising, public relations, events, and more).
Key features and functions of a Centre of Media Practices may include:
- Research and Development: Conducting research to stay abreast of industry trends, emerging technologies, and best practices in media production and communication.
- Training and Education: Offering specialized training programs, workshops, and courses to enhance the skills and knowledge of media professionals, students, and enthusiasts.
- Collaboration and Networking: Facilitating collaboration and networking opportunities among media practitioners, professionals, and organizations to foster innovation and the exchange of ideas.
- Resource Hub: Serving as a centralized resource hub for the latest tools, technologies, and methodologies in media practices. This could include access to state-of-the-art equipment, software, and facilities.
- Quality Standards: Establishing and promoting quality standards and ethical guidelines in media practices to ensure professionalism and integrity within the industry.
- Industry Partnerships: Building partnerships with media organizations, businesses, and educational institutions to create a supportive ecosystem that enhances the overall quality of media practices.
- Incubation and Innovation: Supporting media startups and innovative projects by providing mentorship, funding opportunities, and a conducive environment for creative experimentation.
- Events and Conferences: Organizing conferences, seminars, and events that bring together experts, thought leaders, and practitioners to discuss and share insights on the latest developments in media practices.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with the local community and wider public through outreach programs, public awareness campaigns, and educational initiatives.
- Cross-disciplinary Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between media professionals and experts from other disciplines, such as technology, business, and the arts, to foster interdisciplinary approaches to media practices.
The specific focus and offerings of a Centre of Excellence in Media Practices can vary based on its goals, the scope of the media industry it serves, and the resources available. TIAS, the Department of Journalism and Mass Communication, plays a crucial role in advancing the quality and standards of media-related activities.
Purpose
- A Center of Media Practices typically serves as a hub or focal point of Department of Journalism and Mass Communication dedicated to advancing and promoting best practices in media-related activities. The specific purpose of a Center of Excellence in Media Practices can vary depending on the context.
- Knowledge and Skill Development: Provide training and education programs to enhance the skills of professionals in the media industry. Foster research and development initiatives to stay abreast of emerging trends and technologies in media practices.
- Innovation and Research: Conduct research to identify and implement innovative media practices, technologies, and strategies. Explore and experiment with cutting-edge technologies and methodologies to improve media production and distribution.
- Quality Assurance: Establish and disseminate best practices for maintaining high- quality standards in media content creation. Develop and implement quality assurance processes to ensure the consistent delivery of top-notch media products.
- Collaboration and Networking: Facilitate collaboration among professionals, organizations, and institutions in the media industry. Provide a platform for networking, knowledge exchange, and partnership building within the media community.
- Industry Standards and Guidelines: Contribute to the development and maintenance of industry standards and guidelines for ethical and professional media practices. Work with regulatory bodies to promote and uphold standards in media content creation and distribution.
- Technological Integration: Stay at the forefront of technological advancements in media production, distribution, and consumption. Provide guidance on the integration of new technologies to optimize media workflows and enhance overall efficiency.
- Talent Development: Support the cultivation of talent within the media industry by identifying and nurturing emerging professionals. Collaborate with educational institutions to bridge the gap between academic training and industry requirements.
- Problem Solving and Consultation: Serve as a resource for problem-solving and consultation in areas related to media practices. Offer expertise and advice to address challenges and optimize processes within the media industry.
- Public Outreach and Advocacy: Engage in public outreach and advocacy efforts to promote the value of media practices and their impact on society. Advocate for policies that support the responsible and ethical use of media.
By fulfilling these purposes, a Center of Excellence in Media Practices aims to contribute to the continuous improvement and advancement of the media industry as a whole. It serves as a catalyst for positive change, innovation, and the cultivation of skilled professionals in the ever-evolving field of media.
OBJECTIVES
Centre of Media Practices typically aims to achieve several objectives to promote excellence and innovation in the field of media.
- To conduct research and foster innovation in media practices.
- To provide training and skill development programs for media professionals and students.
- To facilitate collaboration between academia, industry professionals, and other stakeholders.
- To share research findings, best practices, and innovative approaches through publications, conferences, workshops, and other dissemination channels.
- To establish a network of professionals, researchers, and organizations in the media industry.
- To contribute to the development and promotion of quality standards in media practices.
- To promote media literacy initiatives to educate the public about the critical evaluation of media content.
- To support and nurture media-related startups and entrepreneurs.
- To facilitate a culture of continuous learning by organizing workshops, seminars, and training sessions.
- To conduct research that addresses current challenges and opportunities in the media sector.
- To foster a multidisciplinary approach by integrating insights from various fields such as journalism, communication studies, technology, and business.
Center of media Practices
|
EXPERT COMMITTEE
- Dr. Durgesh Tripathi, IP University, Delhi
- Prof. (Dr.) Dilip Kumar, IIMC, J&K
- Mr. Deepak Parvartiyar, Patron and Chief Editor
ADVISORY COMMITTEE
- Prof. Sanjay Dwivedi, Former DG, IIMC, Delhi
- Prof. K G Suresh, VC, MCNUJC, Bhopal
- Prof. Shrikant Singh, MCNUJC, Bhopal
- Prof. Rehman Musawwir, JMI, Delhi
- Prof. Sanjeev Bhanawat, Rajasthan University
ACTIVITIES

Print Media / Print Journalism

Integrated Marketing / Advertising / Public Relations / Events
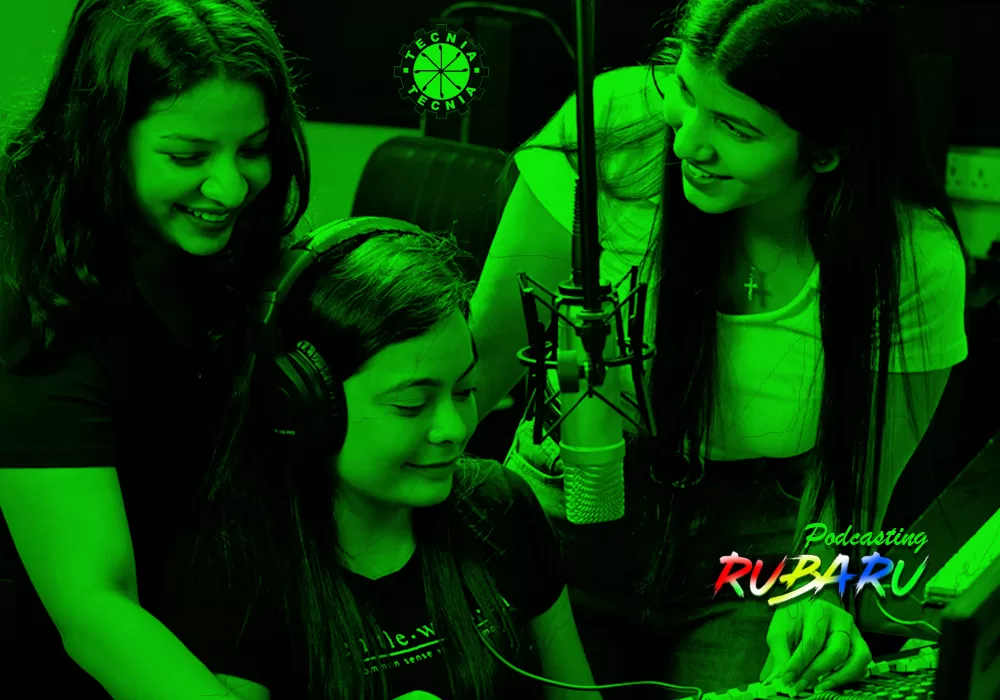

Podcasting / Rubaroo / RJ /VJ

Integrated Marketing / Advertising / Public Relations / Events

New Media / Digital Media

Social Media / Tecnia TV

Media Research & Innovations
Print media, also known as print journalism, refers to the traditional form of media that disseminates information through printed publications. This includes newspapers, magazines, brochures, pamphlets, and other tangible materials. Print journalism has been a prominent source of news and information for centuries, playing a crucial role in shaping public opinion and disseminating knowledge. Here are some key aspects of print media:
- Newspapers: Newspapers are one of the oldest forms of print media, providing daily or weekly coverage of local, national, and international news. They often include various sections such as news, sports, entertainment, business, and opinion columns
- Magazines: Magazines are periodicals that cover a wide range of topics, from fashion and lifestyle to science and politics. They are usually published on a monthly or weekly basis and may include in-depth articles, features, and high-quality images.
- Brochures and Pamphlets: These are shorter printed materials often used for promotional or informational purposes. Businesses, organizations, and government entities use brochures and pamphlets to communicate specific messages to a target audience.
- Journals: Academic and professional journals are print publications that focus on scholarly research and articles within a specific field of study. They play a crucial role in disseminating research findings to the academic community.
- Printing Technology: Advances in printing technology, such as the development of the printing press and later digital printing methods, have significantly impacted the production and distribution of print media. These technologies have made it easier and more cost-effective to produce large quantities of printed materials.
- Circulation and Distribution: Print media is distributed through various channels, including subscription services, newsstands, and online platforms. Circulation numbers indicate the reach of a publication, representing the total number of copies distributed.
- Challenges and Adaptation: Print media has faced challenges in recent years due to the rise of digital media. Many traditional newspapers and magazines have adapted by creating online versions and utilizing digital platforms to reach a broader audience
- Editorial Independence: A cornerstone of print journalism is editorial independence, which involves maintaining a separation between news reporting and external influences, such as advertisers or political interests, to ensure unbiased and accurate reporting.
While digital media has become increasingly prevalent, print journalism continues to have its place, offering a tangible and in-depth reading experience. The coexistence of both print and digital forms allows media organizations to reach diverse audiences and adapt to changing consumer preferences.
Electronic media encompasses various forms of media that utilize electronic or digital technology for the creation, distribution, and transmission of content. This includes broadcasting, film production, and other forms of electronic communication. Here are key aspects of electronic media, broadcasting, and film production:
Broadcasting:
- Television (TV): Television broadcasting involves the transmission of audiovisual content to a mass audience. It includes news programs, entertainment shows, documentaries, and more
- Radio: Radio broadcasting involves the transmission of audio content, including music, news, talk shows, and other programs. It reaches a wide audience and is often used for entertainment, information, and public service announcements.
Film Production:
- Film Industry: Film production is the process of creating motion pictures or films. It involves pre-production (planning and scripting), production (shooting), and post-production (editing and distribution).
- Cinematography: Cinematography is the art and technique of film photography, including the use of cameras, lighting, and other visual elements to create a desired visual effect.
Electronic Communication:
- Internet Broadcasting: With the rise of the internet, broadcasting has expanded to online platforms. Streaming services, podcasts, and online radio stations are examples of internet-based broadcasting.
- Podcasting: Podcasts are digital audio or video files available for streaming or download. They cover a wide range of topics and are accessible to audiences worldwide.
Media Convergence:
- Multimedia Production: The integration of various media forms, such as text, audio, images, and video, is common in electronic media. Multimedia production involves combining these elements for a comprehensive and engaging experience.
- Cross-Platform Content: Many media outlets create content that can be distributed across multiple platforms, including television, radio, online streaming services, and social media.
Digital Technology:
- High Definition (HD) and Ultra High Definition (UHD): Advances in digital technology have led to the widespread adoption of high-quality video formats, enhancing the visual experience for viewers.
- Digital Editing: Post-production in film and broadcasting often involves digital editing tools, allowing for precise editing, special effects, and sound enhancements
Entertainment Industry:
- Content Creation: The entertainment industry encompasses the creation of content for television, film, and online platforms. This includes scripted and unscripted programming, as well as interactive and immersive experiences.
Regulation and Standards:
- Broadcasting Regulations: Many countries have regulatory bodies that oversee broadcasting standards, content, and licensing to ensure ethical and legal practices in the industry.
Electronic media, broadcasting, and film production continue to evolve with technological advancements, providing diverse and dynamic forms of content for global audiences. The convergence of different media forms and the integration of digital technology play significant roles in shaping the landscape of electronic media.
Podcasting: Podcasting is a form of digital media, typically in the form of audio or video files that are available for streaming or download on the internet. Podcasts cover a wide range of topics, from news and education to entertainment and storytelling. Anyone can create a podcast, and it has become a popular medium for individuals and organizations to share their thoughts, expertise, and stories.
Audio media refers to content that is primarily transmitted through auditory channels, such as sound waves. It encompasses various forms of communication and entertainment that rely on audio elements. Here are some key aspects of audio media:
Traditional radio broadcasting involves the transmission of audio signals over the airwaves. It includes news, talk shows, music, interviews, and other forms of programming.
RJ (Radio Jockey):
- RJ(Radio Jockey): An RJ, or Radio Jockey, is a person who hosts a radio show. They are responsible for presenting music, entertaining listeners, and sometimes conducting interviews or discussions on air. RJs often have a distinct style and personality that sets the tone for their shows. They may also engage with listeners through phone calls, messages, or social media.
VJ (Video Jockey):
- VJ(Video Jockey): A VJ, or Video Jockey, is similar to an RJ but in the context of television or online video platforms. A VJ hosts video content, introduces music videos, or presents other visual content. VJs may also conduct interviews, host shows, and engage with the audience through various means, similar to RJs.
Podcasting:
- Podcasting: Podcasting is a form of digital media in which audio files are made available for streaming or downloading through the internet. Podcasts are typically episodic and cover a wide range of topics, including news, education, entertainment, storytelling, and more. Here are some key aspects of podcasting:
Creation and Production:
- Content Planning: Identify your niche or target audience and plan the content accordingly.
- Recording: Use recording equipment such as microphones and headphones to create high-quality audio.
- Editing: Edit the audio files to improve sound quality, remove mistakes, and add any necessary effects or music.
Hosting:
- Choose a Hosting Platform: Select a podcast hosting platform to store and distribute your podcast episodes. Popular choices include Libsyn, Podbean, Buzzsprout, and others.
- RSS Feed: Your hosting platform generates an RSS feed, which allows podcast directories to syndicate your content.
Distribution:
- Submit to Directories: Submit your podcast to directories such as Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Google Podcasts, Stitcher, and others. This increases the visibility of your podcast and makes it accessible to a wider audience.
- Website: Create a website for your podcast where listeners can find additional information, show notes, and links to episodes.
Promotion:
- Social Media: Utilize social media platforms to promote your podcast. Share episode releases, engage with your audience, and create a community around your podcast.
- Collaborations: Collaborate with other podcasters or influencers to cross-promote your content.
- Reviews and Ratings: Encourage listeners to leave reviews and ratings, as positive reviews can attract new listeners
Monetization:
- Sponsorships: Seek sponsorships from businesses or brands related to your podcast’s niche
- Ads and Premium Content: Explore options like premium episodes or exclusive content for paid subscribers
Engaging with Your Audience:
- Feedback: Encourage listener feedback through social media, email, or dedicated listener surveys
- Community Building: Foster a sense of community among your listeners, perhaps through forums, social media groups, or live events.
Consistency:
- Regular Release Schedule: Maintain a consistent release schedule to keep your audience engaged and attract new listeners.
Podcasting is a dynamic and evolving medium, and staying informed about industry trends and continuously improving your content can contribute to the success of your podcast.
Integrated Marketing, Advertising, Public Relations, and Events are distinct but interconnected components of a comprehensive communication strategy for businesses and organizations. When these elements are combined seamlessly, they create a cohesive and powerful approach to reaching and engaging with target audiences. Here’s an overview of each component:
- Integrated Marketing: Integrated Marketing involves coordinating and aligning various marketing channels and communication methods to deliver a unified and consistent message to the target audience.
- Advertising: Advertising is a paid form of communication that promotes products, services, or ideas through various media channels, including print, broadcast, digital, and social media.
- Public Relations (PR): Definition: Public Relations involve managing and cultivating relationships between an organization and its target audience, as well as the broader public. It includes activities like media relations, crisis communication, and reputation management.
- Events: Events refer to organized gatherings or occasions, both physical and virtual, designed to bring people together for a specific purpose. Events can include product launches, conferences, trade shows, and more.
Integration of Components:
- Consistent Messaging: Ensure that the messaging across all components is aligned and reinforces the brand identity
- Cross-Channel Coordination: Integrate marketing efforts across various channels to maximize reach and impact.
- Data and Analytics: Use data to track and analyze the performance of each component, allowing for informed decision-making and optimization.
- Customer Journey: Consider the customer journey and how each component contributes to a seamless and positive experience for the audience.
By integrating these components, organizations can create a holistic communication strategy that maximizes their impact and effectiveness in reaching and engaging with their target audience.
As technology continues to advance, new forms of digital media will likely emerge; shaping the way information is created, consumed, and shared in the future.
Internet and Web-based Platforms:
- Websites: Traditional websites and newer web platforms serve as key components of digital media, providing a wide array of content and services.
- Blogs: Personal and professional blogs have become a popular means of sharing information and opinions online.
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, LinkedIn, and others connect people globally, enabling the sharing of text, images, and videos.
Streaming Services:
- Video Streaming: Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, and others offer on-demand video content.
- Music Streaming: Services like Spotify, Apple Music, and others provide access to a vast library of music.
Digital Publishing:
- E-books and E-readers: Digital books and devices like Kindle have transformed the publishing industry.
- Online Magazines and Newspapers: Many traditional publications have digital counterparts.
Podcasting:
- Podcasts: Podcasts have gained popularity as a form of digital media, allowing individuals and organizations to create and share audio content on various topics.
Gaming:
- Video games: Video games, both online and offline, are a significant part of digital media, with platforms like Steam, PlayStation Network, Xbox Live, and mobile app stores.
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR):
- VR & AR: VR and AR technologies are used for immersive experiences, whether in gaming, education, or virtual tours
Mobile Apps:
- Mobile Applications: Applications for smartphones and tablets cover a wide range of functionalities, from productivity tools to entertainment and social networking.
Digital Advertising:
- Advertising: Online advertising includes various formats such as display ads, video ads, social media ads, and search engine marketing.
User-Generated Content:
- YouTube: Platforms like YouTube and others empower users to create and share their content, contributing to a democratization of media production.
Data and Analytics:
- Digital media: Digital media often involves the collection and analysis of user data for personalized content recommendations, targeted advertising, and improving user experiences
By integrating these components, organizations can create a holistic communication strategy that maximizes their impact and effectiveness in reaching and engaging with their target audience.
Certainly, social media refers to online platforms and websites that allow users to create and share content, connect with others, and participate in virtual communities. These platforms are designed for various purposes, including socializing, networking, entertainment, and information-sharing. Some of the most popular social media platforms as of our knowledge update in January 2022 include:
- Facebook: A widely used platform for connecting with friends and family, sharing updates, and joining groups of common interest
- Instagram: A photo and video-sharing platform known for its visually appealing content and popularity among younger users.
- Twitter: A micro-blogging platform where users share short messages called tweets, often used for real-time updates, news, and discussions.
- LinkedIn: A professional networking platform focused on career and business connections.
- YouTube: While primarily a video-sharing platform, it also serves as a social media platform where users can comment, like, & subscribe to channels.
- Pinterest: A visual discovery and bookmarking platform where users can discover and save ideas for various interests.
- WhatsApp: A messaging app that allows users to send text messages, make voice and video calls, and share media files.
- Flickr:
By integrating these components, organizations can create a holistic communication strategy that maximizes their impact and effectiveness in reaching and engaging with their target audience.
Tecnia TV is a prominent YouTube channel in Bharat. It is owned by the Tecnia Group of Institution. It was founded on July 26, 2017 and known for its extensive Tecnia news coverage, current events, lecture recording in the field of Management Sciences, Information Communication Technology, Journalism and Mass Communication and providing updates on current affairs, politics, business, sports, and entertainment. Tecnia TV is also known for its real-time reporting, breaking news coverage, and a variety of talk shows and programs covering different aspects of news and current events.
Media research and innovations play a crucial role in understanding and shaping the rapidly evolving landscape of communication and information dissemination. Here are some key aspects related to media research and innovations:
1. Audience Analysis:
- Demographics and Psychographics: Understanding the audience’s characteristics and preferences helps media professionals tailor content to specific demographics and psychographics.
- User Behavior: Analyzing how users consume media, interact with platforms, and engage with content provides valuable insights for content creators and advertisers
2. Technological Innovations:
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Integration of VR and AR in media offers immersive experiences, from virtual tours to interactive storytelling.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI enhances content recommendations, personalization, and automates certain aspects of content creation and distribution.
- Blockchain: Enhances transparency, traceability, and security in media transactions, such as content ownership, royalties, and advertising.
3. Content Creation and Distribution:
- Data-Driven Content Creation: Analyzing data to identify trends and preferences helps creators produce content that resonates with their target audience.
- Streaming Services: The rise of on-demand streaming platforms has transformed how people consume media, leading to changes in content creation and distribution strategies
- Podcasting and Voice Technology: The popularity of podcasts and voice-activated devices has influenced content creation and audience engagement.
4. Social Media and Influencer Marketing:
- Analyzing Social Media Trends: Researching social media trends helps media professionals stay relevant and engage with their audience effectively.
- Influencer Marketing Strategies: Leveraging influencers for brand promotion and content dissemination requires understanding audience dynamics and influencer impact.
5. Ethical Considerations:
- Misinformation and Disinformation: Research on combating misinformation and disinformation is vital for maintaining the integrity of media content.
- Privacy Concerns: As technology advances, addressing privacy issues becomes crucial to maintaining trust between media organizations and their audiences.
6. Media Literacy and Education:
- Promoting Media Literacy: Research in this area aims to understand how to educate the public about critically analyzing media content, identifying misinformation, and fostering responsible consumption.
- Educational Technology: Innovations in educational technology can enhance media literacy programs and make learning more engaging
7. Globalization and Cultural Impact:
- Cross-Cultural Communication: Understanding how media content is received and interpreted across different cultures is essential for global media organizations.
- Localization Strategies: Adapting content to local cultural nuances ensures resonance with diverse audiences.
8. Sustainability in Media Production:
- Green Technologies: Research on environmentally friendly production methods and sustainable technologies contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of media production.
- Digital Media vs. Physical Media: Exploring the environmental impact of digital media consumption compared to traditional physical media.
9. Emerging Platforms:
- Metaverse and Extended Reality: The exploration of the metaverse and extended reality platforms presents new opportunities for media content and user interaction.
10. Metrics and Measurement:
- Analytics and KPIs: Developing and refining metrics for assessing the success of media campaigns, content performance, and audience engagement.