Value added courses
- INTRODUCTION
- HINDI TYPING
- PHOTOGRAPHY
- PROFESSIONAL LEARNING OF PR & ADVERTISING
- DIGITAL MEDIA MARKETING (BASICS)
- DIGITAL MEDIA MARKETING (ADVANCED)
- VISUAL COMMUNICATION DESIGN
- WEB JOURNALISM
- SPORT COMMENTARY AS A PROFESSION
- COPYWRITING
- MOJO
- COMPUTING SKILLS
- COMMUNICATIVE ENGLISH
- DATA JOURNALISM
INTRODUCTION
Value-Added courses are part of the curriculum that is aimed to educate students with the skills; they need to enhance their employability quotient and equipped them with the abilities they need to succeed in life. The BAJMC Department of Tecnia Institute of Advanced Studies, Rohini, New Delhi has established a variety of value-added courses in order to enhance students’ existing skill sets and match them with industry expectations. These courses will be led by professionals or in-house personnel, and they will help students stand out in the job market by adding value to their CV. These programmes typically have sessions once a semester, allowing students to pursue them without disrupting their normal degree course work
| DJMC-VAC-01 | HINDI TYPING | Credits:2 |
Pre-Requisites
- A system containing ‘Mangal Font’ for the practice of Hindi Typing.
- Basic understanding of Hindi Grammar.
- Basic sense and understanding of News Writing.
- Basic knowledge of different reporting beats.
INTRODUCTION
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the Hindi Media Houses and Organizations.
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the role of Hindi Content Writer.
- To develop an understanding about the mannerism of Hindi News Writing.
- To develop writing skills from the employability perspective for the role of Content Writer and as well as for the News Reporter and Writer
Learning Outcomes
- Students would be prepared from the perspective of employability for the Hindi Media Houses and Organizations.
- Students would be prepared from the perspective of employability for the role of Hindi Content Writer.
- Students would be having an understanding about the mannerism of Hindi News Writing.
- Students would be having writing skills from the employability perspective for the role of Content Writer and as well as for the News Reporter and Writer
How to Download Mangal font
Mangal Font is a Devnagari Script Font or Hindi Font which is based upon Unicode. Or in other terms it’s most common Unicode Hindi font widely used for Hindi Typing or Media Industry. Mangal Font is by default install in Windows Operating System You can check in your system go to Control Panel -> Fonts -> Search for Mangal you will find it. If Your PC or Laptop have not Mangal font in your Device then download it’s free on Google Platform.
- Download the font from Google Fonts, or another font website.
- Unzip the font by double-clicking on the.
- Open the font folder, which will show the font or fonts you downloaded.
- Open the folder, then right-click on each font file and select Install.
- Your font should now be installed!
Introduction of Hindi Keyboard(Mangal)

Hindi Word spelling knowledge
(हिंदी वर्तनी शुद्धि) किसी शब्द को लिखने मे प्रयुक्त वर्णोँ के क्रम को वर्तनीया अक्षरी कहते है । अँग्रेजी मे वर्तनी को‘Spelling’ तथा उर्दू मे ‘हिज्जे’ कहते है । उच्चारण दोष अथवा शब्द रचना के नियमों की जानकारी की अपर्याप्तता के कारण सामान्यतः वर्तनी अशुद्धि हो जाती है ।- उच्चारण दोष: कई क्षेत्रो व भाषाओ मे, स–श, व–ब, न–ण आदि वर्णो मे अर्थ भेदन ही किया जाता तथा इनके स्थान पर एक ही वर्णस, बयान बोला जाता है, जबकि हिन्दी मे इन वर्णो की अलग–अलग अर्थ –भेदक ध्वनियाँ है । अतः उच्चारण दोष के कारण इनके लेखन मे अशुद्धि हो जाती है ।
- अक्षर रचना की जानकारी का अभाव:देवनागरी लिपि मे संयुक्त व्यंजनो मे दो व्यंजन मिलाकर लिखे जाते है, परन्तु इनके लिखने मे त्रुटि हो जाती है ।
The movement of fingers on Keyboard
It is important to position your hands on the keyboard correctly. Your fingers must be in the middle row of your keyboard on the “home keys”: Starting with your left hand, place your little finger on key A, ring finger on S, middle finger on D and index finger on F. Your thumb must rest on the Space bar.
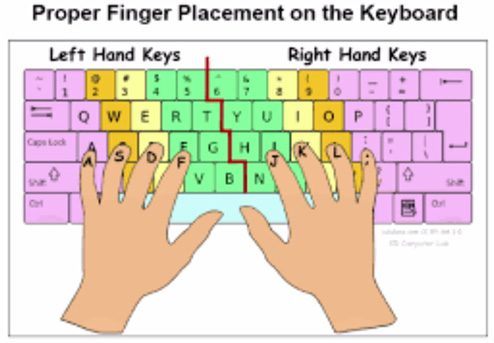
Instructions of Typewriting in Mangal font
How to type Single word, double words and Sentence using of Mangal font & how to type special in Hindi using of Mangal font.
Speed Practice / Practical Training
Students Will practices sentence and improve their Speed in Hindi typing
Assignments (Weekly Based)
Every Week Students will work on typing Assignment & Submit to Resource Person.
Note :Hindi Typing Value Added Course will carry total 15 hours (Weekly 5 Hours: 4 Hours Lecture & 1 Hour Assignment)
उद्देश्य :
समाचार की अवधारणा, समाचार मूल्य की पहचान और समाचार लेखन की प्रक्रिया से परिचय कराना, रिपोर्टिंग के सैद्धांतिक एवं व्यावहारिक ज्ञान से अवगत कराना, विद्यार्थियों को प्रिंट पत्रकारिता के लिए लिखने के लिए सक्षम बनाना, इसके लिए सूचना संग्रहण प्रसंस्करण और प्रेषण कौशल का प्रशिक्षण देने पर जोर रहेगा |
समाचार लेखन
|
References
- Paramount Hindi Typing Practice Book (Mangal Font) by Paramount authors
- Puja Computer Hindi Typing (Mangal & kruti Dev Font) (Unicode Inscript Keyboard) by Navjeevan
- Lekhak Kaise Banein (Hindi Translation: How to be a Writer) by Ruskin Bond (Author), Reenu Talwar (Translator)
- समाचार: लेखन एवं रिपोर्टिंग – News: Writing and Reporting by Publisher: Shivalik Prakashan
| DJMC-VAC-02 | PHOTOGRAPHY | Credits:2 |
Pre-Requisites
- Students should have a clear vision about the idea of photography.
- They should have focused point of view and clear vision towards anything to click a photo.
- They should have little bit of journalistic and communication skills as an aspiring photo journalist
INTRODUCTION
- To define Photography and all about its exposure and composition
- To explain all about the lenses and various streams of photography
- To describe the parts of a digital camera and their functions
- To describe various lights and lighting applications
- To demonstrate proficiency of knowledge in Photo Journalism
Learning Outcomes
On completion of this course students would be able to get knowledge about camera and its parts. They can do photography with in-depth knowledge of its composition, exposure and depth of field. It would be easy for the students to use Cameras in best way in all situations. They would be able to use various kinds of lights according to the requirement of photography. They would become a professional photographer in various areas. They would have an opportunity to open their own photo studio. They can work as photojournalist in media houses.Detail Contents
|
References :
- Read This If You Want to Take Great Photographs by Henry Carroll
- Langford’s Basic Photography: The guide for serious photographers by Michael Langford
- Extraordinary Everyday Photography by Brenda Tharp and Jed Manwaring
| DJMC-VAC-03 | PROFESSIONAL LEARNING OF PR & ADVERTISING | Credits:2 |
Pre-Requisites
- Basic understanding of Public Relations.
- Basic understanding of Advertising.
- Fundamental idea of Strategic Communication.
- General understanding of Creativity for Advertising.
- Idea of role of PR in Public Sector.
INTRODUCTION
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the role of PR in Public Sector.
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the Advertising Industry.
- To develop an understanding about the creative aspects of Advertising.
- To develop visual literacy and basic consumer behavioral understanding from employability perspective.
Learning Outcomes
- Students will be prepared from the perspective of employability for the role of PR in Public Sector.
- Students will be prepared from the perspective of employability for the Advertising Industry.
- Students will be having an understanding about the creative aspects of Advertising.
- Students will be having and understanding of visual literacy and basic consumer behaviour from employability perspective
Detail Contents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References :
- Indian Parliamentary Democracy by U.N. Gupta
- Public Service Announcements: Rambling Thought to Help You in This Complex World: Rambling thoughts to help you in this complex world by M.d. Stanley, Kenneth J.
- Ogilvy on Advertising by David Ogilvy
- Visual Persuasion: The Role of Images in Advertising by Paul Messaris
- The Case for Creativity, by James Hurman
| DJMC-VAC-02 | DIGITAL MARKETING | Credits:4 |
Pre-Requisites​​
- Students should have knowledge of online marketing fundamentals and advertising via online media such as print, digital, internet marketing
Objectives​​
The main objective of this course to make participants understand the online business models and digital marketing methodology from the point of view of consumers, entrepreneurs. Moreover, the course aims at understanding the student’s different techniques of digital marketing so that they can utilize this technique to support organization’s marketing activities
LEARNING Outcomes
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to:
- Different techniques of promotion on online platforms
- Internet marketing communication techniques
- Interpret the traditional marketing mix within the context of a changing and extended range of digital strategies and tactics.
- Comprehend the importance of conversion and working with digital relationship marketing
GGSIPU UNIVERSITY Syllabus
Detail Contents
|
List of Suggested Books​​
- 1. Chaffey, D, Ellis-Chadwick, F, Johnston, K. and Mayer, R, (4th Ed.,2009) Internet Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice, Third Edition, Pearson Education, New Delhi.
- Strauss, Judy and Frost, Raymond (6th Ed, 2011), E-Marketing, 5th Edition, PHI Learning, New Delhi.
- Roberts, M, L,.(3rd Ed, 2013) Internet Marketing, 1st Indian Edition, Cengage Learning, New Delhi
- Shainash G, and Jagdish N Sheth (1st Ed, 2008). Customer Relationship Management- A Strategic Perspective, Macmillan India Ltd
| DJMC-VAC-02 | DIGITAL MARKETING | Credits:4 |
Pre-Requisites​​
- Students should qualify basic level of digital marketing and must have the knowledge of marketing platforms for advertising via online media such as print, digital, internet marketing
Objectives​​
The main objective of this course is to make goals, plan campaigns, and reach customers. Understand what keeps customers engaged between attention and action Modify current business operations to provide a better online experience. Master the science of measuring performance versus plan. Grasp the Project management skills. Know how to continuously improve performance to increase ROI with data and analytics.to support organization’s marketing activities.
LEARNING Outcomes
On successful completion of the course, the students will be able to:
- Know different techniques of SEO
- Understand the target audience by using different tools
- Hands-on experience on different promotional techniques.
- Learn advanced promotional techniques by using different online marketing tools and channels.
GGSIPU UNIVERSITY Syllabus
Detail Contents
|
List of Suggested Books​​
- The psychology of email marketing Influencing subscribers and driving engagement Author: Eleanor Blake Year: 2023
- Strauss, Judy and Frost, Raymond (6th Ed, 2011), E-Marketing, 5th Edition, PHI Learning, New Delhi.
- Chaffey, D, Ellis-Chadwick, F, Johnston, K. and Mayer, R, (4th Ed.,2009) Internet Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice, Third Edition, Pearson Education, New Delhi.
- Shainash G, and Jagdish N Sheth (1st Ed, 2008). Customer Relationship Management- A Strategic Perspective, Macmillan India Ltd.
- The Art Of SEO: Mastering Search Engine Optimization by Eric Enge of Stone Temple Consulting, Stephan Spencer, and Jessie C. Stricchiola.
| DJMC-VAC-05 | VISUAL COMMUNICATION DESIGN | Credits:2 |
Pre-Requisites
- Basic understanding of Visual Communication Design
- Understanding about elements, principles and Typography of design in different forms of visual and graphic communication for Print, Electronic and Web Media
INTRODUCTION
- Apply knowledge gained of designing soft-wares for design and layout
- Demonstrate proficiency of skills in designing and creating layouts using page layout software for visual media
Learning Outcomes
- Students would be able to print designer, book designer, type designer, illustrator, environmental graphic designer, advertising, web designer, motion designer, animator, game designer, experience designer
Course Content :
Graphic Design Course syllabus designed by Tecnia is completely based on the current industrial requirement of the companies with real project workDetail Contents
|
References :
- Davis, M.(2012). Graphic Design Theory. London: Thames& Hudson
- Joss, M., Nelson, L. (1977). Graphic Design Tricks & Techniques. Cincinnati, OH: North Light Books.
- Sarkar, N. N. (1998). Designing Print Communication. New Delhi: S. Publications.
- Sarkar, N. N. (2012). Art and Print Production. Oxford. University Press.
- http://design.tutsplus.com/graphic Design Illustration Tutorials
| DJMC-VAC-06 | WEB JOURNALISM | Credits:2 |
Pre-Requisites
- Students must understand technological advances and they should be an active user of Internet.
- Students should notice the new changes and keep ready themselves to deal with it
- Students should know the technical jargons and vocabulary required in the field
- Students must go through the writing skills and should have the reading ability of contents available on the websites
INTRODUCTION
- To provide an in depth understanding of New technological innovations and upgradations in Web journalism
- To showcase the significance of Web journalism and its implications on masses concerned with it
- To give an overview about the law and ethics of Web journalism
- To develop the skills of writing, design, and presentation on Web journalism
Learning Outcomes
- Students would be able to fulfil the industry requirements as per new emerging upgradations in the field
- Students would understand the intricacies involved in the field of Web journalism
- Students can manage their own websites from journalism point of view
- Students would well understand the regulations and law working in the field and showcase their skills at different platforms
Course Content :
References :
| DJMC-VAC-07 | SPORT COMMENTARY AS A PROFESSION | Credits:2 |
PRE-REQUISITES
- Students should have the interest in sports and its technical aspects.
- Students should know about the history, and gradual development of sport and all other components related to it.
- Students should understand the career prospects and the sincerity required for this field.
- Students should have the excellent command on language and skills required for this profession.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To provide them understanding regarding sports and its technical aspects.
- To give an overview of history and the gradual development of sport along with its essential components.
- To prepare them for the career requirements and sincerity required for this field.
- To provide them an opportunity to develop command on language and skills required for this profession.
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students would be able to understand sports and its technical aspects.
- Students would get an overview of history and the gradual development of sport along with its essential components.
- Students would be able to meet the career requirements and sincerity required for this profession.
- Students would be able to develop their command on language and skills which would meet the industry demands.
Detail Contents
|
References :
- Schultz, Brad & Ed Arke (2015), Sports Media, Routledge publication.
- Miller, James Andrew & Tom Shales (20110), Those Guys Have All the Fun – Inside the World of ESPN, LITTLE, BROWN AND COMPANY, London.
- https://bookauthority.org/books/best-sports-broadcasting-books
| DJMC-VAC-08 | COPYWRITING | Credits:2 |
PRE-REQUISITES
- A formal qualification in communications and journalism
- Intermediate to Advance English speaking and writing skills.
- Basic understanding of copywriting.
- Basic understanding of Advertising.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the role of copywriter in the industry.
- To make students understand the industry trends and the competition in the market.
- To develop an understanding of the various aspects of Copywriting.
- To develop techniques, attributes and nuances that are important in the writing field
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students will learn to research which is very important to understand the industry trends and the competition in the market to create an effective ad copy.
- Students will be exposed to the characteristics of good copywriting. They will also be taught the difference between good copywriting and good writing.
- Students will be taught techniques, attributes and nuances that are important in the writing field.
- Students will understand the best copywriting practices that will help them recognize social trends and stay relevant. It is very important for them to their writing fresh and to grow their vocabulary.
Detail Contents
|
References :
- McGraw-Hill Handbook of English Grammar and Usage.
- The Elements of Style.
- BreaktHourough Advertising by Eugene Schwartz
- Made to Stick by Dan and Chip Heath
- Finding the Right Message by Jennifer Havice
- How to Write a Good Advertisement by Vic Schwab
| DJMC-VAC-09 | MOJO | Credits:2 |
PRE-REQUISITES
- Basic understanding of Journalism.
- Basic understanding of Mobile.
- Fundamental idea of Mass communication and communication tools.
- General understanding of Citizen Journalism.
COURSE OBJECTIVES
- To prepare students from the perspective of employability for the role of Citizen Journalist.
- To develop an understanding about the Journalistic aspects tHourough Mobile Journalism.
- To make the students capable to Use Mobile devices to research and report on news developments.
- To make the students capable to use Mobile gear and apps in the field to tell compelling visual stories.
- To make the students capable to Plan, cover and present news in real-time on live-blogging platform, working in teams and using a range of mobile techniques and tools.
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students would be prepared from the perspective of employability for the role of Citizen Journalist.
- Students would have an understanding about the Journalistic aspects tHourough Mobile Journalism.
- Students would be capable to Use Mobile devices to research and report on news developments.
- Students would be capable to use Mobile gear and apps in the field to tell compelling visual stories.
- Students would be capable to Plan, cover and present news in real-time on live-blogging platform, working in teams and using a range of mobile techniques and tools.
Detail Contents
|
References
- MOJO: The Mobile Journalism Handbook How to Make Broadcast Videos with an IPhone Or IPad By Ivo Burum, Stephen Quinn.
- Mobile and Social Media Journalism A Practical Guide By Anthony Adornato.
- Mobile-First Journalism Producing News for Social and Interactive Media By Steve Hill, Paul Bradshaw.
- Mobile Storytelling A Journalist ́s Guide to the Smartphone Galaxy By Björn Staschen, Wytse Vellinga.
| DJMC-VAC-10 | COMPUTING SKILLS | Credits:2 |
INTRODUCTION
Certification in computing skills is a formal recognition of an individual’s competency and expertise in various aspects of computer technology and software applications. In today’s increasingly digital world, the demand for individuals with strong computing skills has grown significantly. This certification of 30 hours serves as a validation of a students’ ability to perform specific tasks and make informed decisions in the realm of information technology.
PRE-REQUISITES
- A system containing different practice i.e. MS Office for practice.
- Basic understanding of computer system.
- Basic knowledge of different computing software.
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students would be able to achieve competence in the use of software, and various computing tools commonly used in the journalism field.
- Students would be prepared from the perspective of employability for the Media Houses and Organizations.
- Students would be having an understanding about the different computing software.
Detail Contents
|
References
- Wempen, F. (2014). Computing Fundamentals: Digital Literacy Edition. United Kingdom: Wiley.
- Introducing Computing: A Guide for Teachers. (2014). United States: Taylor & Francis.
- Wempen, F. (2014). Computing Fundamentals: Introduction to Computers. Germany: Wiley.
- Wempen, F. (2014). Computing Fundamentals: IC3 Edition. Germany: Wiley.
| DJMC-VAC-11 | COMMUNICATIVE ENGLISH | Credits:2 |
INTRODUCTION
Certification in Communicative English is a formal recognition of an individual’s proficiency in using the English language for effective communication. It’s a valuable credential that demonstrates a person’s ability to understand, speak, read, and write English in various real- life contexts, such as social interactions, academic pursuits, and professional environments.
This 30-hour course covers a variety of topics such as grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, listening comprehension, speaking, reading, and writing. Each module is designed to meet the specific needs of the student, helping them to build their fluency and confidence. It also focuses on utilizing the language in real-life situations and in the workplace, helping learners to communicate effectively in English.
PRE-REQUISITES
Prer-equisites for Communicative English course:
- Basic understanding of English grammar
- An outlook towards macro and micro english language skills
- A basic understanding of language and its applications
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students would be able to improve their English language skills through an active learning environment.
- Students would be able to participate in conversations, understand native English speakers better, and express themselves clearly and accurately.
- Students would be able to acquire competence to secure jobs in any area related to Journalism and Mass Communication.
- This course would help students to groom their personality, improve upon spoken English, and techniques to face for job.
Detail Contents
|
References
- Bhatnagar, N., Bhatnagar, M. (2010). Communicative English for Engineers and Professionals:. India: Pearson Education India.
- English and Communication Skills. (2021). (n.p.): Abhishek Publications.
- Shaikh, F. (2016). Communicative English for Intermediate Level. (n.p.): CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform.
- Anohar, B., John, A. (2018). Pursue English Through Communication: Communicative English. (n.p.): Amazon Digital Services LLC – KDP Print US.
| DJMC-VAC-12 | DATA JOURNALISM | Credits:2 |
INTRODUCTION
Certification in Data Journalism is a specialized credential that recognizes an individual’s proficiency in the field of journalism with a particular focus on data analysis, data visualization, and storytelling. This certification program equips students with the skills and knowledge necessary to effectively gather, analyze, and present data-driven stories in an era where data plays a crucial role in news reporting.
PRE-REQUISITES
- A basic understanding of data concepts, such as data types and data sources.
- A basic understanding of statistics can be helpful when interpreting data and identifying trends.
- Understanding the basics of journalism principles, storytelling, and news reporting is advantageous.
- A good understanding of digital tools for data analysis and visualization, such as data visualization software, online data sources, and content management systems.
Learning OUTCOMES
- Students would be able to collect, assess, and validate various types of data from a range of sources, including government databases, online repositories, and private datasets.
- Students will develop the ability to perform basic data analysis, including calculating descriptive statistics, identifying trends, and recognizing patterns within datasets.
- Students would be proficient in weaving data into compelling narratives that engage and inform the audience effectively, transforming data into stories that are understandable and relatable.
- Students will understand and apply ethical standards when working with data, including issues related to data privacy, bias, and responsible reporting.
Detail Contents
|
References
- Digital Investigative Journalism: Data, Visual Analytics and Innovative Methodologies in International Reporting, Oliver Hahn and Florian Stalph.
- Journalism in the Data Age, Dr. Jingrong Tong.
- Bradshaw P. (2018). Data journalism teaching, fast and slow. Asia Pacific Media Educator, 28(1), 55–66. https://doi.org/10.1177/1326365X18769395.
- Anderson C. W. (2018). Apostles of certainty: Data journalism and the politics of doubt. Oxford University Press.