- INTRODUCTION
- PRINCIPLES
- MISSION
- OBJECTIVES
- ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
- FACILITIES & EQUIPMENT
- POLICIES & PROCEDURES
- VAC – AI & ROBOTICS (BASICS)
- VAC – AI & ROBOTICS (ADVANCED)
- CHAIR-COMMITEE-MOM
- DOWNLOADS
- LINKAGES
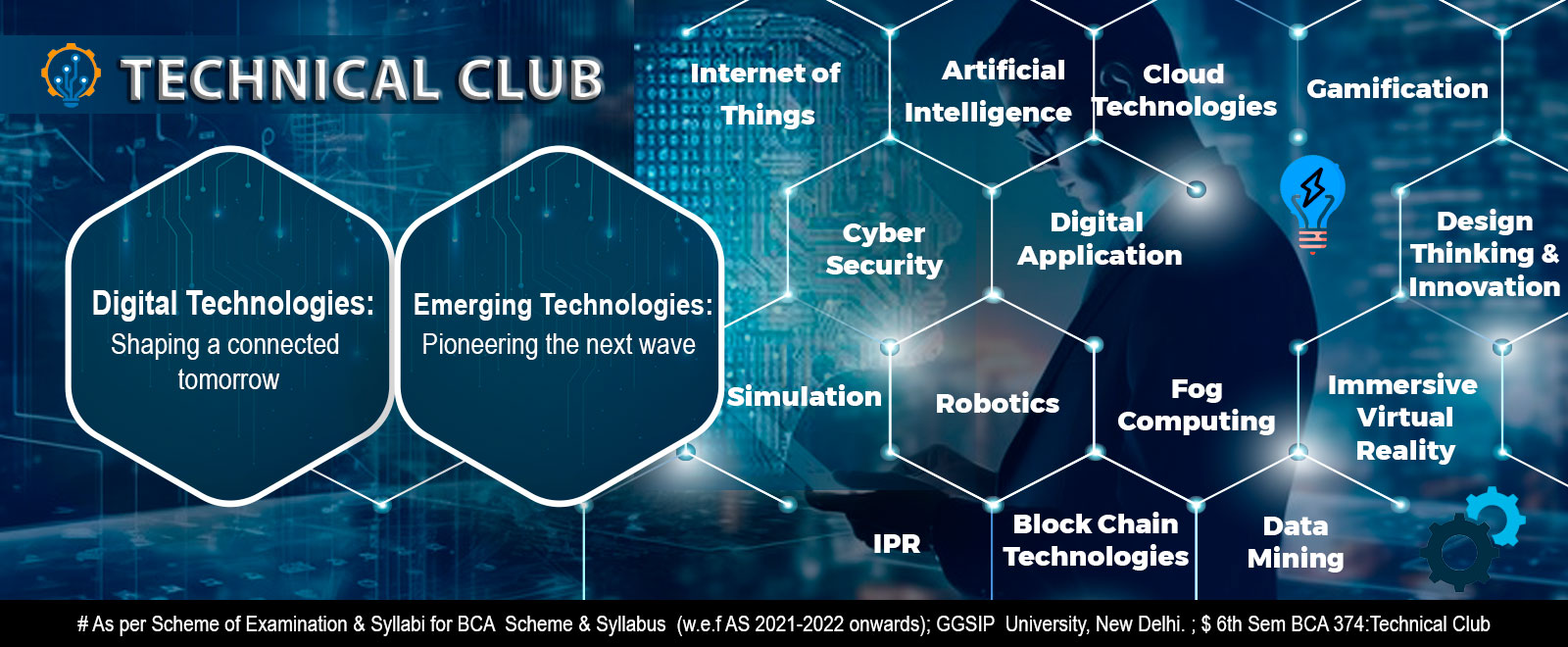
- TECHNICAL CLUB
- IPR CELL – KAPILA
Introduction
The Center of AI and Robotics (COAIR) is a dynamic, multidisciplinaryhub for advancing the frontiers of artificial intelligence and robotics.COAIR is a research and education facility establishment of theInstitute is engaged in education and training program, researchprojects, extension activities, awareness programs and outreachinitiatives related to the development and application of artificialintelligence and robotics technologies which focuses on the conductof R&D in the field, with a special emphasis on command and controlsystems, information and communication technologies, securecommunications, and information management systems with amission to build a pool of trained and dedicated professionals whocan contribute to the development of programme for artificialintelligence and robotics technologies, through this the center aimsto drive research, education, innovation, foster collaboration, thatpositively impact society.
In a significant recent development, artificial intelligence androbotics technologies has been included as a thrust areas of AICTETraining and Learning (ATAL) Academy FDPs/CPDPs. COAIR will betraining various batches of BCA, MCA and other allied areas viatraining program, research projects, extension activities andawareness programs
PRINCIPLES
- Embrace Resilience – Adopt novel ideas and learn from failures
- Take Calculated Risks – Learn from “failure” to diminishuncertainty and make substantive progress
- Process Prioritizing – Focus on doing the work well andcontinually improves the capabilities.
- Inclusive Work Culture – Develop and enables different ideasand innovative thinking to make way for a creatively, technicallyinnovative environment.
- User Interphase – Develop technologies on the bases of user’sneeds.
- Ethics and Integrity – Ensure the highest integrity in all that wedo.
MIssion
The mission of the Center of AI and Robotics is to:
- Conduct cutting-edge research in artificial intelligence, machinelearning, and robotics.
- Develop innovative applications of AI and robotics technologiesto solve real-world problems.
- Provide educational programs and training on AI and roboticsfor students, researchers, and industry professionals.
- Foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing betweenacademia, industry, and the broader AI/robotics community.
- Engage with the public to promote understanding of AI androbotics
OBJECTIVES
The primary objectives of the center are:
- Develop and design technologies to increase the effectivenessand resiliency of information systems.
- Reliably deliver excellent performance systems in high pressureand resource-impacted IT environments.
- Keep track of evolving challenges in cyber security.
- Assure conformance to national technology policy – critical toassure national security and self-sufficiency.
- Advance the state-of-the-art in AI and robotics through originalresearch
- Create novel AI-powered robotic systems and applications
- Train the next generation of AI and robotics experts
- Facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration and technology transfer
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
The Center of AI and Robotics has following working divisions:
- R&D – Responsible for conducting fundamental and appliedresearch in AI and robotics.
- Prototyping– Focuses on the design, development, and testingof AI-powered robotic systems.
- Education and Training – Provides educational programs,workshops, and courses on AI and robotics.
- Outreach and Partnerships – Manages the center's externalcollaborations, industry partnerships, and public engagementactivities.
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT
The Research and Development division is responsible for conductingboth fundamental and applied research in AI and robotics.Key focus areas include:
- Machine learning and deep learning
- Natural language processing and generation
- Computer vision and perception
- Robotic control and planning
- Human-robot interaction
- Ethical and societal implications of AI and robotics
Researchers are encouraged to pursue interdisciplinarycollaborations, both within the center and with external partners.The division also manages a competitive internal grant program tofund promising research projects.
PROTOTYPING
The Prototyping division is responsible for the design, development,and testing of AI-powered robotic systems. Key activities include:
- Conceptual design and system architecture development
- Mechanical, electrical, and software engineering of roboticcomponents
- Rapid prototyping and iterative development
- Integration of AI/ML algorithms with robotic hardware
- Comprehensive testing and performance evaluation
The division maintains a well-equipped workshop and fabricationfacility to support the entire product development lifecycle, frominitial concept to functional prototypes.
EDUCATION & TRAINING
The Education and Training division is responsible for developing anddelivering educational programs on AI and robotics. Key offeringsinclude:
- Undergraduate and graduate-level courses
- Professional development workshops and short courses
- Online learning modules and virtual training
- Hands-on training on robotic hardware and software
- Internship and fellowship opportunities
The division collaborates closely with academic departments andindustry partners to ensure the curriculum remains relevant andaligned with emerging trends and workforce needs.
OUTREACH & PARTNERSHIPS
The Outreach and Partnerships division is responsible for the center'sexternal engagement and collaboration activities. Key responsibilitiesinclude:
- Organizing public lectures, demonstrations, and communityevents
- Participating in industry conferences and trade shows
- Managing partnerships with corporate, government, and non-profit organizations
- Facilitating technology transfer and commercialization of centerinnovations
- Securing research grants and funding from external sources
The division also oversees the center's communications, marketing,and media relations to promote the center's work and raise itsprofile within the broader AI and robotics community.
FACILITIES & EQUIPMENT
The Center of AI and Robotics is housed in a dedicated building thatincludes the following facilities:-
- Classrooms and lecture halls for educational programs
- Collaborative workspaces and meeting rooms
- Administrative offices and support services
Proposed
- Autonomous systems testing and evaluation spaces
- AI Research lab with high-performance computing infrastructure
- Robotics design and fabrication workshops
- Advanced AI/ML software and hardware (e.g., GPUs, TPUs)
- Robotic platforms and components (e.g., manipulators, mobilebases, sensors)
- 3D printers, CNC machines, and other fabrication tools
- Virtual and augmented reality systems for visualization andsimulation
POLICIES & PROCEDURES
The Center of AI and Robotics has a comprehensive set of policiesand procedures that govern the day-to-day operations of the facility.These include, but are not limited to:
- Safety and security protocols
- Facility usage and access guidelines
- Procurement and inventory management
- Intellectual property and data management
- Human resources and personnel policies
- Budget and financial management
- Travel and expense reimbursement
- Visitor and guest access procedures
| ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & ROBOTICS (BASICS) | L | T | P | Credits |
| 2 | – | – | 2 |
Objectives
Artificial Intelligence is a major step forward in how computer system adapts, evolves and learns. It has widespread application in almost every industry and is considered to be a big technological shift, similar in scale to past events such as the industrial revolution, the computer age, and the smart phone revolution.
This course will give an opportunity to gain expertise in one of the most fascinating and fastest growing areas of Computer Science through classroom program that covers fascinating and compelling topics related to human intelligence and its applications in industry, defense, healthcare, agriculture and many other areas. This course will give the students a rigorous, advanced and professional graduate-level foundation in Artificial Intelligence. The objective of this course is to impart knowledge about industrial robots for their control and design.
Pre-Requisites
- Basic Programming in Python
- Data Structures
- Basic Engineering Mathematics
- Automation and Control
Learning Outcomes
After undergoing this course, the students will be able to:
- Build intelligent agents for search and games
- Solve AI problems through programming with Python
- Learning optimization and inference algorithms for model learning
- Design and develop programs for an agent to learn and act in a structured environment.
- Perform kinematic and dynamic analyses with simulation.
- Design control laws for a robot.
- Integrate mechanical and electrical hardware for a real prototype of robotic device.
- Select a robotic system for given application.
Detail Contents
| Topic | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Concept of AI, history, current status, scope, agents, environments, Problem Formulations, Review of tree and graph structures, State space representation, Search graph and Search tree. | (3 Hours) |
| Search Algorithms | Random search, Search with closed and open list, Depth first and Breadth first search, Heuristic search, Best first search, A* algorithm, Game Search. | (9 Hours) |
| Probabilistic Reasoning | Probability, conditional probability, Bayes Rule, Bayesian Networks- representation, construction and inference, temporal model, hidden Markov model. | (12 Hours) |
| Introduction to Robotics | 1.1 Types and components of a robot, Classification of robots, closed-loop and open- loop control systems. 1.2 Kinematics systems; Definition of mechanisms and manipulators, Social issues and safety. | (7 Hours) |
| Robot Kinematics and Dynamics | 2.1 Kinematic Modelling: Translation and Rotation Representation, Coordinate transformation, DH parameters, Jacobian, Singularity, and Statics 2.2 Dynamic Modelling: Equations of motion: Euler-Lagrange formulation | (10 Hours) |
| Sensors and Vision System | 3.1 Sensor: Contact and Proximity, Position, Velocity, Force, Tactile etc. 3.2 Introduction to Cameras, Camera calibration,Geometry of Image formation, Euclidean/Similarity/Affine/Projective transformations 3.3 Vision applications in robotics. | (13 Hours) |
List of Suggested Books
- Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” , 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall
- Elaine Rich and Kevin Knight, “Artificial Intelligence”, Tata McGraw Hill
- Trivedi, M.C., “A Classical Approach to Artifical Intelligence”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Saroj Kaushik, “Artificial Intelligence”, Cengage Learning India, 2011
- David Poole and Alan Mackworth, “Artificial Intelligence: Foundations for Computational Agents”, Cambridge University Press 2010.
- Saha, S.K., “Introduction to Robotics, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New Delhi, 2014.
- Ghosal, A., “Robotics”, Oxford, New Delhi, 2006.
- Niku Saeed B., “Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Systems, Applications”, PHI, New Delhi.
- Mittal R.K. and Nagrath I.J., “Robotics and Control”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Mukherjee S., “Robotics and Automation”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Craig, J.J., “Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control”, Pearson, New Delhi, 2009
- Mark W. Spong, Seth Hutchinson, and M. Vidyasagar, “Robot Modelling and Control”, John Wiley and Sons Inc, 2005
- Steve Heath, “Embedded System Design”, 2nd Edition, Newnes, Burlington, 2003
- Merzouki R., Samantaray A.K., Phathak P.M. and Bouamama B. Ould, “Intelligent Mechatronic System: Modeling, Control and Diagnosis”, Springer.
Websites for Reference
| ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & ROBOTICS (ADVANCED) | L | T | P | Credits |
| 1 | – | 2 | 2 |
Objectives
Artificial Intelligence is a major step forward in how computer system adapts, evolves and learns. It has widespread application in almost every industry and is considered to be a big technological shift, similar in scale to past events such as the industrial revolution, the computer age, and the smart phone revolution.
This course will give an opportunity to gain expertise in one of the most fascinating and fastest growing areas of Computer Science through classroom program that covers fascinating and compelling topics related to human intelligence and its applications in industry, defense, healthcare, agriculture and many other areas. This course will give the students a rigorous, advanced and professional graduate-level foundation in Artificial Intelligence. The objective of this course is to impart knowledge about industrial robots for their control and design.
Pre-Requisites
- Basic Programming in Python
- Data Structures
- Basic Engineering Mathematics
- Automation and Control
- Perform kinematic and dynamic analyses with simulation.
- Design control laws for a robot.
- Integrate mechanical and electrical hardware for a real prototype of robotic device.
- Select a robotic system for given application.
Learning Outcomes
After undergoing this course, the students will be able to:
- Build intelligent agents for search and games
- Solve AI problems through programming with Python
- Learning optimization and inference algorithms for model learning
- Design and develop programs for an agent to learn and act in a structured environment.
Detail Contents
| Topic | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Markov Decision process | MDP formulation, utility theory, utility functions, value iteration, policy iteration and partially observable MDPs. | (10 Hours) |
| Reinforcement Learning | Random search, Search with closed and open list, Depth first and Breadth first search, Heuristic search, Best first search, A* algorithm, Game Search. | (10 Hours) |
| Robot Control | 4.1 Basics of control: Transfer functions, Control laws: P, PD, PID 4.2 Non-linear and advanced controls | (12 Hours) |
| Robot Actuation Systems | Actuators: Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic; Transmission: Gears, Timing Belts and Bearings, Parameters for selection of actuators | (8 Hours) |
| Control Hardware and Interfacing | Embedded systems: Architecture and integration with sensors, actuators, components, Programming for Robot Applications | (10 Hours) |
List of Practicals
- Write a programme to conduct uninformed and informed search.
- Write a programme to conduct game search.
- Write a programme to construct a Bayesian network from given data.
- Write a programme to infer from the Bayesian network.
- Write a programme to run value and policy iteration in a grid world.
- Write a programme to do reinforcement learning in a grid world.
List of Suggested Books
- Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” , 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall
- Elaine Rich and Kevin Knight, “Artificial Intelligence”, Tata McGraw Hill
- Trivedi, M.C., “A Classical Approach to Artifical Intelligence”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Saroj Kaushik, “Artificial Intelligence”, Cengage Learning India, 2011
- David Poole and Alan Mackworth, “Artificial Intelligence: Foundations for Computational Agents”, Cambridge University Press 2010.
- Saha, S.K., “Introduction to Robotics, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New Delhi, 2014.
- Ghosal, A., “Robotics”, Oxford, New Delhi, 2006.
- Niku Saeed B., “Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Systems, Applications”, PHI, New Delhi.
- Mittal R.K. and Nagrath I.J., “Robotics and Control”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Mukherjee S., “Robotics and Automation”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Craig, J.J., “Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control”, Pearson, New Delhi, 2009
- Mark W. Spong, Seth Hutchinson, and M. Vidyasagar, “Robot Modelling and Control”, John Wiley and Sons Inc, 2005
- Steve Heath, “Embedded System Design”, 2nd Edition, Newnes, Burlington, 2003
- Merzouki R., Samantaray A.K., Phathak P.M. and Bouamama B. Ould, “Intelligent Mechatronic System: Modeling, Control and Diagnosis”, Springer.
Websites for Reference
- INTRODUCTION
- AI & ROBOTICS (BASICS)
- AI & ROBOTICS (ADVANCED)
- CHAIR-COMMITEE-MOM
- MANUAL
- DOWNLOADS
Introduction
The Artificial Intelligence and robotics are the emerging fields of technology and the blend of these two technologies is the future of the current generation. It seems to be the most dominant blend in the history of industrial innovations. The Center of AI and Robotics proposed Centre of Excellence at Tecnia Institute of Advanced Studies is an initiative taken with the intent of learning about the latest technologies of the field like Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and Robotics. The Centre of AI & Robotics will give students ample opportunities to not only learn about them but also work with them to develop innovative things. An absolute new age of robotization is ready to transform every industrial process of Industry 4.0. AI-driven robots like Drones and AI driven medical instruments are considered more efficient than the old robots that used to work without AI technology. The AI and Robotic development centre will have:
- Establishment
- Process set up
- Training
- Practical knowledge
- Practical demonstration
- Module development
- Creation of Prototype
- Executable Model
- Patent
- Commercial Diffusion
Machine learning conditions the robots in such a way that with timely evolution, they learn from their own mistakes, thus preventing constant human intervention and parallel effort. This ensures adaptability in robotics. Along with these implications, AI and ML powered software products can analyse data from hundreds of sources and can give future predictions about the growth of Industry. AI can analyse consumer data and predict about consumer preferences, product development, and marketing channels. The students from different departments of Tecnia Institute of Advanced Studies are trained on technologies like machine learning, deep learning (a subset of machine learning) and robotics. Scikit-learn provides dozens of built- in Machine Learning algorithms and models, called estimators. Each estimator can be fitted to some data using its fit method. Scikit-learn is used by the students to create and evaluate the new model. TensorFlow is a low-level library that is also used by the students to implement machine learning techniques and algorithms.
| ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & ROBOTICS (BASICS) | L | T | P | Credits |
| 2 | – | – | 2 |
Objectives
Artificial Intelligence is a major step forward in how computer system adapts, evolves and learns. It has widespread application in almost every industry and is considered to be a big technological shift, similar in scale to past events such as the industrial revolution, the computer age, and the smart phone revolution.
This course will give an opportunity to gain expertise in one of the most fascinating and fastest growing areas of Computer Science through classroom program that covers fascinating and compelling topics related to human intelligence and its applications in industry, defense, healthcare, agriculture and many other areas. This course will give the students a rigorous, advanced and professional graduate-level foundation in Artificial Intelligence. The objective of this course is to impart knowledge about industrial robots for their control and design.
Pre-Requisites
- Basic Programming in Python
- Data Structures
- Basic Engineering Mathematics
- Automation and Control
Learning Outcomes
After undergoing this course, the students will be able to:- Build intelligent agents for search and games
- Solve AI problems through programming with Python
- Learning optimization and inference algorithms for model learning
- Design and develop programs for an agent to learn and act in a structured environment.
- Perform kinematic and dynamic analyses with simulation.
- Design control laws for a robot.
- Integrate mechanical and electrical hardware for a real prototype of robotic device.
- Select a robotic system for given application.
Detail Contents
| Topic | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Concept of AI, history, current status, scope, agents, environments, Problem Formulations, Review of tree and graph structures, State space representation, Search graph and Search tree. | (3 Hours) |
| Search Algorithms | Random search, Search with closed and open list, Depth first and Breadth first search, Heuristic search, Best first search, A* algorithm, Game Search. | (9 Hours) |
| Probabilistic Reasoning | Probability, conditional probability, Bayes Rule, Bayesian Networks- representation, construction and inference, temporal model, hidden Markov model. | (12 Hours) |
| Introduction to Robotics | 1.1 Types and components of a robot, Classification of robots, closed-loop and open- loop control systems. 1.2 Kinematics systems; Definition of mechanisms and manipulators, Social issues and safety. | (7 Hours) |
| Robot Kinematics and Dynamics | 2.1 Kinematic Modelling: Translation and Rotation Representation, Coordinate transformation, DH parameters, Jacobian, Singularity, and Statics 2.2 Dynamic Modelling: Equations of motion: Euler-Lagrange formulation | (10 Hours) |
| Sensors and Vision System | 3.1 Sensor: Contact and Proximity, Position, Velocity, Force, Tactile etc. 3.2 Introduction to Cameras, Camera calibration,Geometry of Image formation, Euclidean/Similarity/Affine/Projective transformations 3.3 Vision applications in robotics. | (13 Hours) |
List of Suggested Books
- Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” , 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall
- Elaine Rich and Kevin Knight, “Artificial Intelligence”, Tata McGraw Hill
- Trivedi, M.C., “A Classical Approach to Artifical Intelligence”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Saroj Kaushik, “Artificial Intelligence”, Cengage Learning India, 2011
- David Poole and Alan Mackworth, “Artificial Intelligence: Foundations for Computational Agents”, Cambridge University Press 2010.
- Saha, S.K., “Introduction to Robotics, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New Delhi, 2014.
- Ghosal, A., “Robotics”, Oxford, New Delhi, 2006.
- Niku Saeed B., “Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Systems, Applications”, PHI, New Delhi.
- Mittal R.K. and Nagrath I.J., “Robotics and Control”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Mukherjee S., “Robotics and Automation”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Craig, J.J., “Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control”, Pearson, New Delhi, 2009
- Mark W. Spong, Seth Hutchinson, and M. Vidyasagar, “Robot Modelling and Control”, John Wiley and Sons Inc, 2005
- Steve Heath, “Embedded System Design”, 2nd Edition, Newnes, Burlington, 2003
- Merzouki R., Samantaray A.K., Phathak P.M. and Bouamama B. Ould, “Intelligent Mechatronic System: Modeling, Control and Diagnosis”, Springer.
Websites for Reference
| ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & ROBOTICS (ADVANCED) | L | T | P | Credits |
| 1 | – | 2 | 2 |
Objectives
Artificial Intelligence is a major step forward in how computer system adapts, evolves and learns. It has widespread application in almost every industry and is considered to be a big technological shift, similar in scale to past events such as the industrial revolution, the computer age, and the smart phone revolution.
This course will give an opportunity to gain expertise in one of the most fascinating and fastest growing areas of Computer Science through classroom program that covers fascinating and compelling topics related to human intelligence and its applications in industry, defense, healthcare, agriculture and many other areas. This course will give the students a rigorous, advanced and professional graduate-level foundation in Artificial Intelligence. The objective of this course is to impart knowledge about industrial robots for their control and design.
Pre-Requisites
- Basic Programming in Python
- Data Structures
- Basic Engineering Mathematics
- Automation and Control
- Perform kinematic and dynamic analyses with simulation.
- Design control laws for a robot.
- Integrate mechanical and electrical hardware for a real prototype of robotic device.
- Select a robotic system for given application.
Learning Outcomes
After undergoing this course, the students will be able to:- Build intelligent agents for search and games
- Solve AI problems through programming with Python
- Learning optimization and inference algorithms for model learning
- Design and develop programs for an agent to learn and act in a structured environment.
Detail Contents
| Topic | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Markov Decision process | MDP formulation, utility theory, utility functions, value iteration, policy iteration and partially observable MDPs. | (10 Hours) |
| Reinforcement Learning | Random search, Search with closed and open list, Depth first and Breadth first search, Heuristic search, Best first search, A* algorithm, Game Search. | (10 Hours) |
| Robot Control | 4.1 Basics of control: Transfer functions, Control laws: P, PD, PID 4.2 Non-linear and advanced controls | (12 Hours) |
| Robot Actuation Systems | Actuators: Electric, Hydraulic and Pneumatic; Transmission: Gears, Timing Belts and Bearings, Parameters for selection of actuators | (8 Hours) |
| Control Hardware and Interfacing | Embedded systems: Architecture and integration with sensors, actuators, components, Programming for Robot Applications | (10 Hours) |
List of Practicals
- Write a programme to conduct uninformed and informed search.
- Write a programme to conduct game search.
- Write a programme to construct a Bayesian network from given data.
- Write a programme to infer from the Bayesian network.
- Write a programme to run value and policy iteration in a grid world.
- Write a programme to do reinforcement learning in a grid world.
List of Suggested Books
- Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig, “Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach” , 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall
- Elaine Rich and Kevin Knight, “Artificial Intelligence”, Tata McGraw Hill
- Trivedi, M.C., “A Classical Approach to Artifical Intelligence”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Saroj Kaushik, “Artificial Intelligence”, Cengage Learning India, 2011
- David Poole and Alan Mackworth, “Artificial Intelligence: Foundations for Computational Agents”, Cambridge University Press 2010.
- Saha, S.K., “Introduction to Robotics, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill Higher Education, New Delhi, 2014.
- Ghosal, A., “Robotics”, Oxford, New Delhi, 2006.
- Niku Saeed B., “Introduction to Robotics: Analysis, Systems, Applications”, PHI, New Delhi.
- Mittal R.K. and Nagrath I.J., “Robotics and Control”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- Mukherjee S., “Robotics and Automation”, Khanna Publishing House, Delhi.
- Craig, J.J., “Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control”, Pearson, New Delhi, 2009
- Mark W. Spong, Seth Hutchinson, and M. Vidyasagar, “Robot Modelling and Control”, John Wiley and Sons Inc, 2005
- Steve Heath, “Embedded System Design”, 2nd Edition, Newnes, Burlington, 2003
- Merzouki R., Samantaray A.K., Phathak P.M. and Bouamama B. Ould, “Intelligent Mechatronic System: Modeling, Control and Diagnosis”, Springer.
Websites for Reference
- Webpage Incharge : Dr. Rajesh Kumar